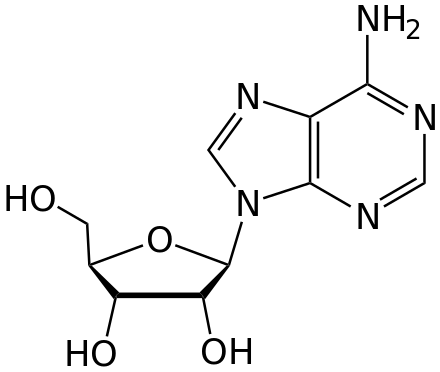
Adenosine is a purine nucleoside composed of a molecule of adenine attached to a ribose sugar molecule (ribofuranose) moiety via a β-N9-glycosidic bond. Derivatives of adenosine are widely found in nature and play an important role in biochemical processes, such as energy transfer—as adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP)—as well as in signal transduction as cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). Adenosine itself is a neuromodulator, believed to play a role in promoting sleep and suppressing arousal. Adenosine also plays a role in regulation of blood flow to various organs through vasodilation.